CoMOLA
CoMOLA is a python tool for optimal spatial allocation of land uses. The tool creates optimal land-use maps for up to four objectives. It takes into account constraints and can be coupled with external models to evaluate different objectives (e.g. ecosystem services/biodiversity models)
Cite this software
Description
About
CoMOLA (Constrained Multi-objective Optimization of Land use Allocation) is a free Python tool to optimize the allocation of land use for multiple objectives. It builds upon the open source "inspyred" Python library and includes functions for reading, encoding and writing land use maps as well as genome generation and repair mutation algorithms for considering constraints during the optimization procedure. It runs on Windows and Linux and allows for the integration of any model whose prediction (e.g. a value for an ecosystem service) is based on a land use raster map. In its basic form, CoMOLA can be used immediately by inputting a raster map representing the status-quo land use, ready-to-run models written in R including their input data, and (optional) information on constraints. As constraints, the tool can consider (1) transition rules defining which type of land use can be converted into which other type and (2) minimum and maximum area proportions of each land use type within the study area. All relevant settings, such as paths to input data and models as well as optimization-specific parameters (e.g. population size, crossover and mutation rates) and settings related to constraint-handling and raster map-analysis are managed in one single control file (Fig. 1).
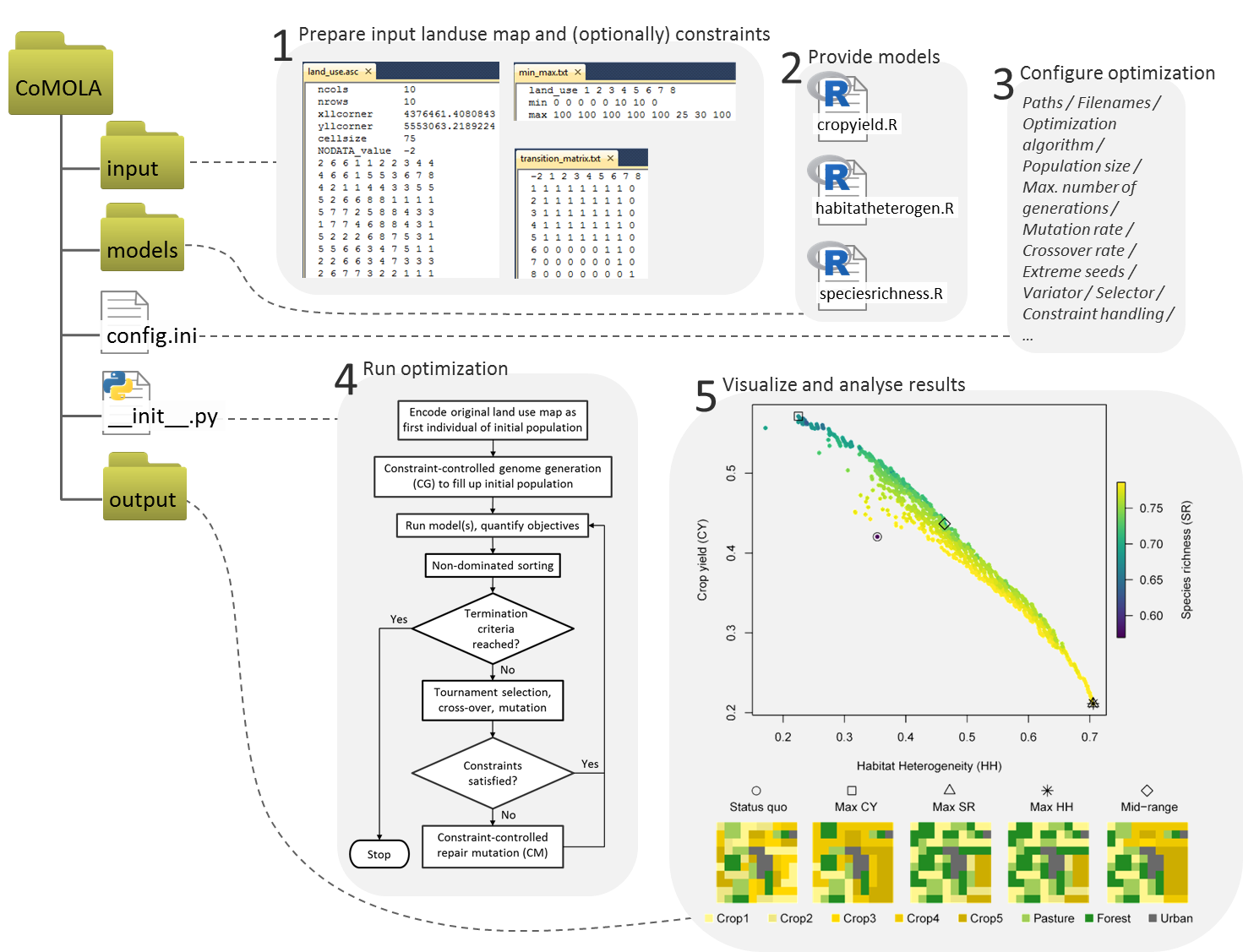
Fig. 1: CoMOLA framework.
Fields of application
Fields of application have been e.g. the spatial allocation of agricultural land uses such as different types of cropland and grassland maximizing yield, biodiversity and minimizing nutrient leaching, the optimal allocation of riparian reforestation efforts along rivers, exploring optimal strategies to retain water and nutrients in agricultural catchments. Other potential fields of application can be nature conservation, climate adaptation, restoration, urban planning, renewable energies or even other contexts outside of environmental research where spatial allocation of certain measures/uses are required.
Teaching
CoMOLA has been used for teaching spatial multi-objective optimization at universities. For these purposes, a Docker container is available (instructions can be found in the GitHub repository).
Requirements
Installation
CoMOLA was developed and tested for Python 3.9 and above.
- Required Python packages
- matplotlib
Furthermore R has to be installed to run external models.
Input
CoMOLA requires different types of spatial and non-spatial input data (e.g. land-use map, patch-ID map, transition rules). For details, check the GitHub repository.
Output
Once CoMOLA has been started, a log file is generated in the output folder documenting the process of optimization.
A successful run of CoMOLA will provide the following outputs:
- fitness values for the best solutions
- ascii maps for the best solutions
- the genome and fitness values of all individuals tested in the optimization
An R-script is provided in the GitHub repository to extract, evaluate and plot the best solutions (see Fig. 2).
Example plot:

Fig. 2: Example plot of optimization output.
Participating organisations
Reference papers
- 1.Author(s): Felix Witing, Marie Anne Eurie Forio, Francis J. Burdon, Brendan Mckie, Peter Goethals, Michael Strauch, Martin VolkPublished in Journal of Applied Ecology by Wiley in 2022, page: 1456-147110.1111/1365-2664.14176
- 2.Author(s): Moritz Hildemann, Judith A. VerstegenPublished in Environmental Modelling & Software by Elsevier BV in 2021, page: 10506910.1016/j.envsoft.2021.105069
- 3.Author(s): Andrea Kaim, Michael Strauch, Martin VolkPublished in Frontiers in Water by Frontiers Media SA in 202010.3389/frwa.2020.579087
- 4.Author(s): Nina Schwarz, Falk Hoffmann, Sonja Knapp, Michael StrauchPublished in Frontiers in Environmental Science by Frontiers Media SA in 202010.3389/fenvs.2020.00016
- 5.Author(s): Bartosz Bartkowski, Michael Beckmann, Martin Drechsler, Andrea Kaim, Veronika Liebelt, Birgit Müller, Felix Witing, Michael StrauchPublished in Frontiers in Environmental Science by Frontiers Media SA in 202010.3389/fenvs.2020.00103
- 6.Author(s): Michael Strauch, Anna F. Cord, Carola Pätzold, Sven Lautenbach, Andrea Kaim, Christian Schweitzer, Ralf Seppelt, Martin VolkPublished in Environmental Modelling & Software by Elsevier BV in 2019, page: 241-25110.1016/j.envsoft.2019.05.003
- 7.Author(s): Willem Verhagen, Emma H. van der Zanden, Michael Strauch, Astrid J.A. van Teeffelen, Peter H. VerburgPublished in Environmental Science & Policy by Elsevier BV in 2018, page: 186-19610.1016/j.envsci.2018.03.013
Mentions
- 1.Author(s): Werner HärdtlePublished in Biodiversität, Ökosystemfunktionen und Naturschutz by Springer Berlin Heidelberg in 2024, page: 587-84310.1007/978-3-662-68236-4_7
- 2.Author(s): Katrin Karner, Hermine Mitter, Martin SchönhartPublished in Alpine Landgesellschaften zwischen Urbanisierung und Globalisierung by Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden in 2022, page: 211-22710.1007/978-3-658-36562-2_12
- 3.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 38-4810.1017/9781108662963.005
- 4.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 88-9710.1017/9781108662963.010
- 5.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 60-7410.1017/9781108662963.008
- 6.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 3-510.1017/9781108662963.003
- 7.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 294-29810.1017/9781108662963.025
- 8.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 138-15710.1017/9781108662963.015
- 9.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 269-29310.1017/9781108662963.024
- 10.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 75-8710.1017/9781108662963.009
- 11.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 158-18010.1017/9781108662963.016
- 12.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 206-21810.1017/9781108662963.020
- 13.Author(s): Marije Schaafsma, Bartosz BartkowskiPublished in Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals, Life on Land by Springer International Publishing in 2020, page: 1-1110.1007/978-3-319-71065-5_117-1
- 14.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 181-19210.1017/9781108662963.017
- 15.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 111-12710.1017/9781108662963.013
- 16.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 262-26810.1017/9781108662963.023
- 17.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 219-24010.1017/9781108662963.021
- 18.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 128-13710.1017/9781108662963.014
- 19.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 195-20510.1017/9781108662963.019
- 20.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 241-26110.1017/9781108662963.022
- 21.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 98-10810.1017/9781108662963.011
- 22.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 6-3710.1017/9781108662963.004
- 23.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 109-19210.1017/9781108662963.012
- 24.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 49-10810.1017/9781108662963.006
- 25.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 193-26810.1017/9781108662963.018
- 26.Author(s): Marije Schaafsma, Bartosz BartkowskiPublished in Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals, Life on Land by Springer International Publishing in 2020, page: 1022-103210.1007/978-3-319-95981-8_117
- 27.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 51-5910.1017/9781108662963.007
- 28.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: 1-4810.1017/9781108662963.002
- 1.Author(s): Savya Sachi, Ajay Kumar Singh, Arpit Jain, Suman Devi, Yogesh Kumar Sharma, Senthil AthithanPublished in 2023 Intelligent Methods, Systems, and Applications (IMSA) by IEEE in 2023, page: 276-28010.1109/imsa58542.2023.10217745
- 2.Author(s): Ajay Kumar Singh, Arpit Jain, Divya, Yogesh Kumar Sharma, Senthil Athithan, Savya SachiPublished in 2023 6th International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I) by IEEE in 2023, page: 552-55610.1109/ic3i59117.2023.10397859
- 3.Author(s): P Adlene Ebenezer, A R KavithaPublished in 2021 5th International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA) by IEEE in 2021, page: 320-32510.1109/iceca52323.2021.9676103
- 1.Author(s): Gusiyuan Wang, Wangshu Mu, Changfeng Li, Yuanhui WangPublished in International Journal of Geographical Information Science by Informa UK Limited in 2026, page: 1-3310.1080/13658816.2025.2611984
- 2.Author(s): Solen Le Clec'h, Robert Huber, Robert Finger, Jean-Marc Delore, Franziska J. Richter, Valentin H. KlausPublished in Agricultural Systems by Elsevier BV in 2026, page: 10449010.1016/j.agsy.2025.104490
- 3.Author(s): Imane El Fartassi, Ryan T. Sharp, Victoria A. Bell, Andrew P. Whitmore, Helen Metcalfe, Nathan Missault, John Redhead, David M. Cooper, Jonathan Storkey, Helen Davies, Theo Jackson, Kevin Coleman, Alice E. MilnePublished in Journal of Environmental Management by Elsevier BV in 2026, page: 12838910.1016/j.jenvman.2025.128389
- 4.Author(s): Yuxiang Dong, Anirudh Subramanyam, Hong WuPublished in Environmental Modelling & Software by Elsevier BV in 2026, page: 10675810.1016/j.envsoft.2025.106758
- 5.Author(s): Chuandong Tan, Yusheng Yan, Xiujiao Hu, Xuefei WuPublished in Global Ecology and Conservation by Elsevier BV in 2025, page: e0377510.1016/j.gecco.2025.e03775
- 6.Author(s): Lucía Galán-Cano, Juan Cámara-Aceituno, Manuel Jesús Hermoso-Orzáez, Julio Terrados-CepedaPublished in Applied Sciences by MDPI AG in 2025, page: 940610.3390/app15179406
- 7.Author(s): Sheena Davis, Matthew Grainger, Marion Pfeifer, Zarah Pattison, Philip Stephens, Roy SandersonPublished in Environmental Evidence by Springer Science and Business Media LLC in 202510.1186/s13750-025-00355-8
- 8.Author(s): Regina O’Kelley, Rose A Graves, Holly Amer, Lucas C R SilvaPublished in Environmental Research Letters by IOP Publishing in 2025, page: 08400310.1088/1748-9326/ade5bb
- 9.Author(s): Esteban Menares-Barraza, Nonka Markova-Nenova, Astrid Sturm, Frank Wätzold, Klaus BirkhoferPublished in Biological Conservation by Elsevier BV in 2025, page: 11140110.1016/j.biocon.2025.111401
- 10.Author(s): Ran He, Wenhao Jia, Zhengzhe QianPublished in Water by MDPI AG in 2025, page: 205910.3390/w17142059
- 11.Author(s): Suleiman O. Yakubu, Lynne Falconer, Trevor C. TelferPublished in Aquaculture by Elsevier BV in 2025, page: 74167010.1016/j.aquaculture.2024.741670
- 12.Author(s): Zenith Arnejo, Benoit Gaudou, Mehdi Saqalli, Nathaniel BantayanPublished in Forests by MDPI AG in 2025, page: 129310.3390/f16081293
- 13.Author(s): Hamid Siroosi, Gholam Ali Heshmati, Abdolrassoul SalmanmahinyPublished in Journal of Environmental Management by Elsevier BV in 2025, page: 12351010.1016/j.jenvman.2024.123510
- 14.Author(s): Sydney E. White, Felix Witing, Cordula I.H. Wittekind, Martin Volk, Michael StrauchPublished in Environmental Modelling & Software by Elsevier BV in 2025, page: 10650810.1016/j.envsoft.2025.106508
- 15.Author(s): Juan He, Yao Li, Wei Zhou, Mingjie Qian, Enmao Zha, Xueyi ShiPublished in Land Degradation & Development by Wiley in 2025, page: 3670-368410.1002/ldr.5591
- 16.Author(s): Bin ZhouPublished in Journal of Geographic Information System by Scientific Research Publishing, Inc. in 2025, page: 167-19810.4236/jgis.2025.174009
- 17.Author(s): Tazeen Fatima Khan, Md. Golam Faruque, Bijoya PaulPublished in Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection by Scientific Research Publishing, Inc. in 2025, page: 171-18210.4236/gep.2025.135012
- 18.Author(s): Shuruo Li, Xiaobin Jin, Bo Han, Yaxuan Feng, Shuxin Wu, Zhao Qi, Xiaolin Zhang, Yinkang ZhouPublished in Applied Geography by Elsevier BV in 2025, page: 10369610.1016/j.apgeog.2025.103696
- 19.Author(s): Thomas Knoke, Carola Paul, Elizabeth Gosling, Esther Reith, Peter Annighöfer, Senthold Asseng, Logan Bingham, Lucie Chmelikova, Fabian Frick, Benjamin D. Hafner, Sara Diana Leonhardt, Luisa Menapace, Annette Menzel, Johannes Sauer, Michael Schloter, Kang Yu, Mohsen Zarebanadkouki, Johannes Kollmann, Margit von LützowPublished in Agroforestry Systems by Springer Science and Business Media LLC in 202510.1007/s10457-025-01206-8
- 20.Author(s): Aymeric Oliveira-Xavier, Sophie Calmé, Dominique GravelPublished in Land Use Policy by Elsevier BV in 2025, page: 10757710.1016/j.landusepol.2025.107577
- 21.Author(s): Marta Bonato, Alfred Burian, Juliàn A. Equihua, Anna F. Cord, Bartosz Bartkowski, Michael StrauchPublished in Journal of Environmental Management by Elsevier BV in 2025, page: 12693910.1016/j.jenvman.2025.126939
- 22.Author(s): Jia YuPublished in International Journal of Architectural Computing by SAGE Publications in 202510.1177/14780771251352937
- 23.Author(s): Sarah S. Gall, Tom Harwood, Michael Obersteiner, Jim W. HallPublished in Communications Earth & Environment by Springer Science and Business Media LLC in 202510.1038/s43247-025-02728-w
- 24.Author(s): Sayuri Hernández-Maravilla, María Luisa Castrejón-Godínez, Efraín Tovar-Sánchez, Hugo Albeiro Saldarriaga-Noreña, Alexis Rodríguez, Marcos Eduardo Rosas-Ramírez, Patricia Mussali-GalantePublished in Plants by MDPI AG in 2025, page: 11810.3390/plants14010118
- 25.Author(s): Shihao Zhou, Yilun Qu, Yixiang Wang, Zhaoping Wu, Yan ShiPublished in Resources, Environment and Sustainability by Elsevier BV in 2025, page: 10021110.1016/j.resenv.2025.100211
- 26.Author(s): Eryan Guo, Jing HePublished in Frontiers in Forests and Global Change by Frontiers Media SA in 202510.3389/ffgc.2025.1470065
- 27.Author(s): Xin Li, Zilong Zhao, Xiaodong Ma, Jian Zhang, Haibin XuPublished in Chinese Geographical Science by Springer Science and Business Media LLC in 2025, page: 835-85110.1007/s11769-025-1528-z
- 28.Author(s): Irina Heiß, Friederike Stegmann, Matteo Wolf, Martin Volk, Andrea KaimPublished in Ecological Indicators by Elsevier BV in 2025, page: 11321210.1016/j.ecolind.2025.113212
- 29.Author(s): Junli ShaPublished in Earth Science Informatics by Springer Science and Business Media LLC in 202510.1007/s12145-025-01939-1
- 30.Author(s): Michal Switalski, Maarten Van Strien, Adrienne Grêt-RegameyPublished in Journal of Land Use Science by Informa UK Limited in 2025, page: 61-8110.1080/1747423x.2025.2476942
- 31.Author(s): Xiaohang Bai, Jieping ChenPublished in Grassland Science by Wiley in 2025, page: 136-14610.1111/grs.70006
- 32.Author(s): Matthew G. Kirby, Joanna Zawadzka, Alister J. ScottPublished in Ecosystem Services by Elsevier BV in 2024, page: 10162010.1016/j.ecoser.2024.101620
- 33.Author(s): Cristina Pavanello, Marcello Franchini, Stefano Bovolenta, Elisa Marraccini, Mirco CorazzinPublished in Sustainability by MDPI AG in 2024, page: 421410.3390/su16104214
- 34.Author(s): Daniel Richards, Thomas R. Etherington, Alexander Herzig, Sandra LavorelPublished in Land by MDPI AG in 2024, page: 46010.3390/land13040460
- 35.Author(s): S.M.D. Kinnoumè, Serge Adomou, Gérard Nounagnon Gouwakinnou, Thierry Dèhouégnon HouéhanouPublished in Open Journal of Ecology by Scientific Research Publishing, Inc. in 2024, page: 125-14710.4236/oje.2024.142008
- 36.Author(s): Hanwen Xu, Mark Randall, Lei Li, Yuyi Tan, Thomas BalstrømPublished in Journal of Hydrology by Elsevier BV in 2024, page: 13215410.1016/j.jhydrol.2024.132154
- 37.Author(s): Luis Alberto Bertolucci Paes, Barbara Stolte Bezerra, Daniel Jugend, Fabiana Liar AgudoPublished in Environmental Development by Elsevier BV in 2024, page: 10103910.1016/j.envdev.2024.101039
- 38.Author(s): Jackson Stockbridge, Alice R. Jones, Christopher J. Brown, Mark J. Doubell, Bronwyn M. GillandersPublished in Ecological Applications by Wiley in 202410.1002/eap.3056
- 39.Author(s): Jan-Hendrik Niemann, Stefan Klus, Nataša Djurdjevac Conrad, Christof SchüttePublished in Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena by Elsevier BV in 2024, page: 13405210.1016/j.physd.2024.134052
- 40.Author(s): Robert Huber, Cordelia Kreft, Karin Späti, Robert FingerPublished in Ecological Economics by Elsevier BV in 2024, page: 10830310.1016/j.ecolecon.2024.108303
- 41.Author(s): Anja Heidenreich, Adrian Muller, Philipp Oggiano, Catherine Pfeifer, Simon Moakes, Johan Six, Mathias StolzePublished in Environmental Research Letters by IOP Publishing in 2024, page: 07300510.1088/1748-9326/ad57d3
- 42.Author(s): J. Carlier, M. Doyle, J.A. Finn, D. Ó hUallacháin, S. Ruas, P. Vogt, J. MoranPublished in Science of The Total Environment by Elsevier BV in 2024, page: 17450910.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.174509
- 43.Author(s): Simone Valeri, María F. Schmitz, Belén Acosta-Gallo, Duilio Iamonico, María Villodre, Cecilia Arnáiz-Schmitz, Giulia CapotortiPublished in Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment by Elsevier BV in 2024, page: 10919910.1016/j.agee.2024.109199
- 44.Author(s): Shengjie Yang, Liang Zhong, Yunqiao Zhou, Bin Sun, Rui Wang, Zhengguo Sun, Jianlong LiPublished in Remote Sensing by MDPI AG in 2024, page: 250510.3390/rs16132505
- 45.Author(s): Ruimin Lin, Ru Guo, Yunyang Li, Guanghui Shao, Yuhao Zhang, Kaiming Peng, Xiangfeng HuangPublished in Resources, Conservation and Recycling by Elsevier BV in 2024, page: 10787210.1016/j.resconrec.2024.107872
- 46.Author(s): Xiaotong Xie, Kunlin Wu, Yingchao Li, Shanshan Guo, Xiaoshun LiPublished in Land by MDPI AG in 2024, page: 53710.3390/land13040537
- 47.Author(s): Maulinna Kusumo Wardhani, Daniel Mohammad Rosyid, Akhmad FaridPublished in E3S Web of Conferences by EDP Sciences in 2024, page: 0102810.1051/e3sconf/202449901028
- 48.Author(s): Jawad Ghafoor, Marie Anne Eurie Forio, Indira Nolivos, Mijial Arias-Hidalgo, Peter L. M. GoethalsPublished in Journal of Water and Climate Change by IWA Publishing in 2024, page: 5021-504010.2166/wcc.2024.064
- 49.Author(s): Volker von Groß, Kibrom T. Sibhatu, Alexander Knohl, Matin Qaim, Edzo Veldkamp, Dirk Hölscher, Delphine Clara Zemp, Marife D. Corre, Ingo Grass, Sebastian Fiedler, Christian Stiegler, Bambang Irawan, Leti Sundawati, Kai Husmann, Carola PaulPublished in Journal of Environmental Management by Elsevier BV in 2024, page: 12071010.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120710
- 50.Author(s): Solen le Clech, Lenny G.J. van Bussel, Marjolein E. Lof, Bart de Knegt, István Szentirmai, Erling AndersenPublished in Ecosystem Services by Elsevier BV in 2024, page: 10161610.1016/j.ecoser.2024.101616
- 1.Author(s): Tim G. Williams, Falk Krumbe, Arndt FeuerbacherPublished in 202610.2139/ssrn.6294963
- 2.Author(s): Kristine Bilande, Una Diana Veipane, Aleksejs Nipers, Irina PilverePublished in 202610.3390/land15020204
- 3.Author(s): Shyam George PULICKAN, Pascal LAFON, Laurent LANGLOISPublished by Springer Science and Business Media LLC in 202510.21203/rs.3.rs-7071260/v1
- 4.Author(s): Cesar Rojas, Otalora Martin Low, Riascos Javier, Christopher ScottPublished by Springer Science and Business Media LLC in 202510.21203/rs.3.rs-7464866/v1
- 5.Author(s): Sarah Gall, Tom Harwood, Michael Obersteiner, Jim HallPublished by Springer Science and Business Media LLC in 202510.21203/rs.3.rs-6091509/v1
- 6.Author(s): Thomas Knoke, Carola Paul, Elizabeth Gosling, Esther Reith, Peter Annighöfer, Senthold Asseng, Logan Bingham, Lucie Chmelikova, Fabian Frick, Benjamin Hafner, Sara Diana Leonhardt, Luisa Menapace, Annette Menzel, Johannes Sauer, Michael Schloter, Kang Yu, Mohsen Zare, Johannes Kollmann, Margit von LützowPublished by Springer Science and Business Media LLC in 202410.21203/rs.3.rs-5533706/v1
- 7.Author(s): Grethell Castillo Reyes, René Estrella, Dirk Roose, Floris Abrams, Gerdys Jiménez-Moya, Jos Van OrshovenPublished by Elsevier BV in 202310.2139/ssrn.4601864
- 8.Author(s): Solen Le Clec'h, Robert Huber, Robert Finger, Jean-Marc Delore, Franziska Richter, Valentin H. KlausPublished by Elsevier BV in 202310.2139/ssrn.4669508
- 9.Author(s): Moritz Hildemann, Edzer Pebesma, Judith Anne VerstegenPublished by Research Square Platform LLC in 202210.21203/rs.3.rs-1735209/v1
- 10.Author(s): Daniel HuppmannPublished by Copernicus GmbH in 202110.5194/gmd-2021-76-ec1
- 11.Author(s): Nils Droste, Bartosz Bartkowski, Robert FingerPublished in 2021
- 12.Author(s): Abhijeet MishraPublished by Copernicus GmbH in 202110.5194/gmd-2021-76-ac1
- 13.Author(s): Pekka LauriPublished by Copernicus GmbH in 202110.5194/gmd-2021-76-rc1
- 14.Author(s): Abhijeet MishraPublished by Copernicus GmbH in 202110.5194/gmd-2021-76-ac3
- 15.Author(s): Abhijeet MishraPublished by Copernicus GmbH in 202110.5194/gmd-2021-76-ac2
- 16.Author(s): Walter Rossi CerviPublished by Copernicus GmbH in 202110.5194/gmd-2021-76-rc2
- 17.Published in Ecological-Economic Modelling for Biodiversity Conservation by Cambridge University Press in 2020, page: xiii-xv10.1017/9781108662963.001
- 18.Author(s): Martin DrechslerPublished by Cambridge University Press in 202010.1017/9781108662963
- 19.Author(s): Reed J., Ros-Tonen M., Sunderland T.C.H.Published by Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR) in 202010.17528/cifor/007800
- 20.Author(s): Calum Brown, Ian Holman, Mark RounsevellPublished by Copernicus GmbH in 202010.5194/esd-2020-52
- 21.Author(s): Sam S. Rabin, Peter Alexander, Roslyn Henry, Peter Anthoni, Thomas A. M. Pugh, Mark Rounsevell, Almut ArnethPublished by Copernicus GmbH in 201910.5194/esd-2019-44